Sustainable Manufacturing
LLM as the “cognitive engine” and “interaction interface” for intelligent optimization
Optimization problems in traditional manufacturing systems (e.g., scheduling, process-parameter optimization) typically rely on intelligent optimization (IO) techniques such as genetic algorithms and particle swarm optimization. However, building these algorithmic models is complex, parameter tuning is obscure and hard to master, and the produced “optimal” solutions are often a black box with little intuitive business-level explanation. Heavy dependence on domain experts therefore impedes broad adoption in sustainable manufacturing.
The core of our approach is to position a large language model (LLM) as the “brain” and “translator” of intelligent optimization algorithms, greatly lowering the barrier to use and improving decision quality. Concretely: first, the LLM ingests an engineer’s business description through natural-language interaction (for example, “optimize the production sequence in the painting shop to meet Friday delivery while minimizing VOC emissions and peak energy use”) and automatically translates it into the objective functions and constraints required by a mathematical optimization model. Next, leveraging its strong coding and domain-knowledge capabilities, the LLM automatically invokes or generates appropriate optimization-algorithm scripts to solve the model. Finally — and most critically — the LLM performs multidimensional, interpretable analysis of the solution: it explains the benefits in human language (for example, “this plan schedules energy-intensive steps during nighttime low-price hours, saving an estimated 12% on electricity costs, and reduces paint waste by 15% through batch processing”), and can propose multiple alternative solutions along with trade-off comparisons.
This deep fusion of LLMs and IO not only decentralizes optimization from data scientists to frontline engineers, but—through enhanced explainability—makes sustainability objectives (such as energy saving, emission reduction, and consumption reduction) measurable and trustworthy decision factors, accelerating the practical deployment of green-manufacturing practices.
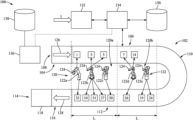
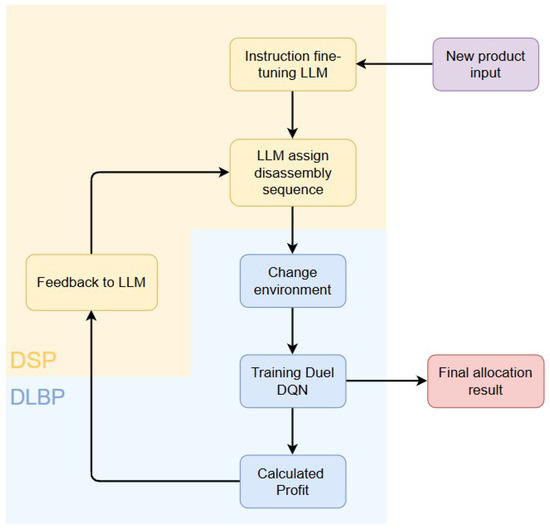
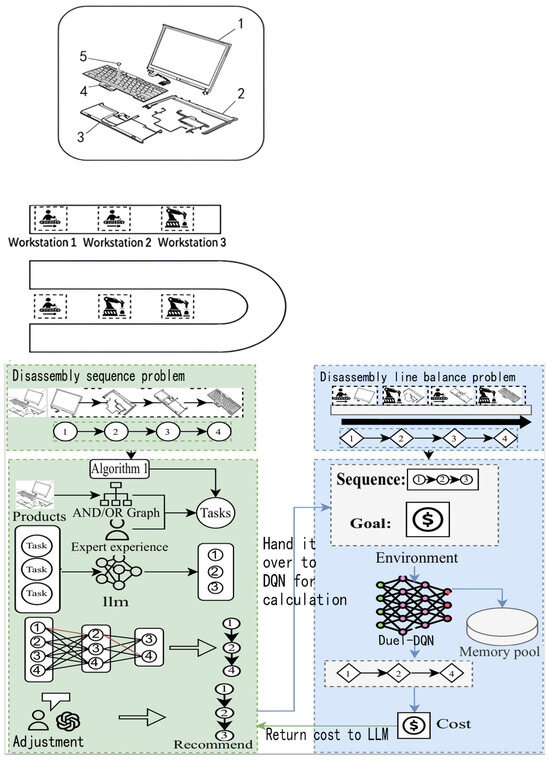
LLM-Assisted Reinforcement Learning for U-Shaped and Circular Hybrid Disassembly Line Balancing in IoT-Enabled Smart Manufacturing
This study proposes a novel U-shaped and circular disassembly line layout, using QLoRA-fine-tuned LLMs and a rebuilt Duel-DQN algorithm to maximize profit under posture constraints, achieving a 26% efficiency gain and near-optimal profitability.
Large Language Model-Assisted Reinforcement Learning for Hybrid Disassembly Line Problem
This research introduces large language model (LLM)-assisted reinforcement learning to optimize task allocation and worker posture in hybrid disassembly lines, reducing convergence iterations by 50% while maintaining high solution quality.
Large AI Models and Their Applications: Classification, Limitations, and Potential Solutions
This paper reviews the rapid development of Large Models (LMs), analyzes key architectural flaws that limit their performance, and discusses potential solutions and future applications in fields like autonomous driving.

System and methods for multi-robotic multi-product U-shaped disassembly line
This paper presents a method to optimize multi-robotic U-shaped disassembly lines, using a mathematical model and an Improved Multi-objective Discrete Brainstorming Optimization (IMDBO) algorithm to maximize profit and minimize the smoothness index.